For Decades, Scientists Puzzled Over The Plastic ‘Missing’ From Our Oceans – But Now It’s Been Found

March 13, 2020
by Britta Denise Hardesty, Principal Research Scientist, Oceans and Atmosphere Flagship, CSIRO and Chris Wilcox, Senior Research Scientist, CSIRO
You’ve probably heard that our oceans have become a plastic soup. But in fact, of all the plastic that enters Earth’s oceans each year, just 1% has been observed floating on the surface. So where is the rest of it?
This “missing” plastic has been a longstanding scientific question. To date, the search has focused on oceanic gyres such as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, the water column (the part of the ocean between the surface and the sea bed), the bottom of the ocean, and the stomachs of marine wildlife.
But our new research suggests ocean plastic is being transported back onshore and pushed permanently onto land away from the water’s edge, where it often becomes trapped in vegetation.
Of course, plastic has been reported on beaches around the world for decades. But there has been little focus on why and how coastal environments are a sink for marine debris. Our findings have big implications for how we tackle ocean plastic.
The hunt for marine pollution
Our separate, yet-to-be-published research has found around 90% of marine debris that enters the ocean remains in the “littoral zone” (the area of ocean within 8km of the coast). This new study set out to discover what happens to it.
We collected data on the amount and location of plastic pollution every 100 kilometres around the entire coast of Australia between 2011 and 2016. Debris was recorded at 188 locations along the Australian coastline. Of this, 56% was plastic, followed by glass (17%) and foam (10%).
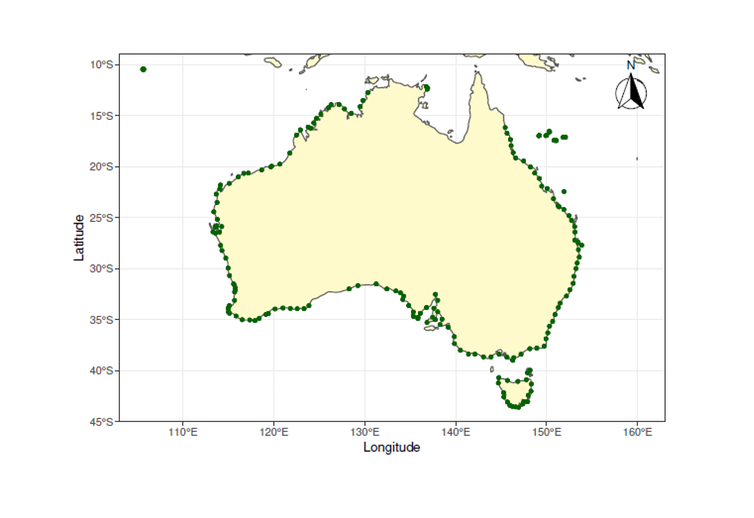
Data was recorded approximately every 100 kilometres along the coast of Australia. Of the marine debris recorded, more than half was plastic.
The debris was a mix of litter from people and deposition from the ocean. The highest concentrations of plastic pollution were found along coastal backshores – areas towards the inland edge of the beach, where the vegetation begins. The further back from the water’s edge we went, the more debris we found.
The amount of marine debris, and where it ends up, is influenced by onshore wave activity and, to a lesser extent, wind activity. Densely populated areas and those where the coast was easily accessible were hotspots for trapped plastics.
Think about what you see on your beach. Smaller debris is often found near the water’s edge, while larger items such as drink bottles, plastic bags and crisp packets are often found further back from the water, often trapped in vegetation.
We also found more debris near urban areas where rivers and creeks enter the ocean. It could be that our trash is being trapped by waterways before it gets to the sea. We’re finding similar patterns in other countries we’re surveying around the Asia Pacific and beyond.
This pollution kills and maims wildlife when they mistake it for food or get tangled in it. It can damage fragile marine ecosystems by smothering sensitive reefs and transporting invasive species and is potentially a threat to human health if toxins in plastics make their way through the food chain to humans.
It can also become an eyesore, damaging the economy of an area through reduced tourism revenue.
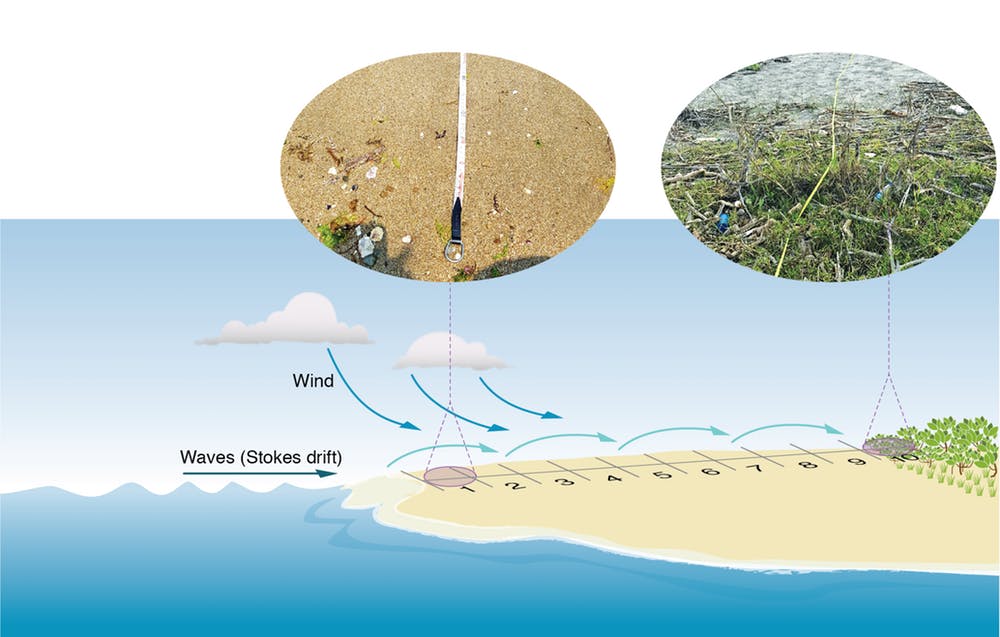
Onshore waves, wind and areas with denser human populations influences where and how much marine debris there is along our coastlines. CSIRO
Talking rubbish
Our findings highlight the importance of studying the entire width of coastal areas to better understand how much, and where, debris gets trapped, to inform targeted approaches to managing all this waste.
Plastic pollution can be reduced through local changes such as water refill stations, rubbish bins, incentives and awareness campaigns. It can also be reduced through targeted waste management policies to reduce, reuse and recycle plastics. We found container deposit schemes to be a particularly effective incentive in reducing marine pollution.
This discussion is particularly timely. The National Plastics Summit in Canberra last week brought together governments, industry and non-government organisations to identify new solutions to the plastic waste challenge, and discuss how to meet targets under the National Waste Policy Action Plan. Understanding that so much of our debris remains local, and trapped on land, provides real opportunities for successful management of our waste close to the source. This is particularly critical given the waste export ban starting July 1 at the latest.
Plastic in our oceans is increasing. It’s clear from our research that waste management strategies on land must accommodate much larger volumes of pollution than previously estimated. But the best way to keep plastic from our ocean and land is to stop putting it in.
Arianna Olivelli contributed to this article, and the research upon which it was based. This article was published first in The Conversation, click here to read the original report - republished under a Creative Commons licence.

CSIRO researcher Denise Hardesty inspects debris on North Stradbroke Island. - Picture courtesy CSIRO.
Ocean Plastic Returning To Aussie Coastlines
March 11, 2020
Plastic waste in the ocean is making its way back to land and increasing pollution on Australia’s beaches, according to new research from CSIRO, Australia’s national science agency.
It explains why estimates of waste entering the ocean each year are 100 times larger than the amount of plastic observed floating on the surface, and suggests waste management strategies on land need to accommodate larger volumes of pollution than previously estimated.
Dr Denise Hardesty is a Principal Research Scientist with CSIRO, working to solve the plastic pollution crisis by reducing unmanaged plastic leaking into the environment.
“We collected data on the amount and location of plastic pollution every 100 kilometres around the entire coast of Australia between 2011 and 2016,” Dr Hardesty said.
“The highest concentrations of marine debris were found along the coastal backshores, where the vegetation begins.”
Arianna Olivelli from Utrecht University, who led the analysis, said these findings indicate that coasts are a major sink for marine debris, particularly for larger debris items.
“The debris recorded along the coasts was found to be a mix of littering and deposition from the ocean,” Ms Olivelli said.
“The results suggest that plastic is moving from urban areas into the ocean, and then being transported back onshore, and pushed onto land, where it remains.
“Onshore wind and waves, together with more densely populated areas, influences the amount and distribution of marine debris. The further back we went from the water’s edge, the more debris we found.”
Wave activity has a much stronger effect than wind in determining where debris ends up.
These findings highlight the importance of including the entire width of coastal areas in studies to understand how much – and where – debris gets trapped.
This is critical for developing targeted waste management policies, particularly in areas with large regional populations, to reduce litter ending up in our oceans and along our coasts.
The study is published in Environmental Research Letters, available at Coastal margins and backshores represent a major sink for marine debris: insights from a continental-scale analysis
Previously Published Here CSIRO Plastics In Marine Environment Reports/ Studies:
- Mapping marine debris around Australia - April 2014
- Australia's Waters Are Full Of Plastic, and We Put It There - September 2014
- Plastic in 99 percent of seabirds by 2050 - September 2015
- World's Largest Marine Pollution Project - June 2017
- How Much Plastic Does It Take To Kill A Turtle? - Very Little - September 2018
- Balloons Are The Number 1 Marine Debris Risk Of Mortality For Our Seabirds - March 2019